Lowering Your Blood Pressure Naturally with Potassium
Maintaining a healthy blood pressure is essential for overall well-being. High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can lead to various health complications. While medications are available to manage hypertension, incorporating natural methods into your lifestyle can also be effective. One such method is increasing your potassium intake. In this article, we will explore the benefits of potassium and how it can help lower your blood pressure naturally.
Understanding Blood Pressure
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the measurement of the force exerted by blood against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it throughout your body. It is typically expressed as two numbers: systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. The systolic pressure is the higher number and indicates the force when your heart contracts and pushes blood out, while the diastolic pressure is the lower number and represents the force when your heart is at rest and refilling with blood. Together, these measurements provide important information about the health and functioning of your cardiovascular system.
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as systolic/diastolic, such as 120/80 mmHg. The systolic pressure represents the pressure during a heartbeat, while diastolic pressure represents the pressure between heartbeats.
The Impact of High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, can have severe consequences for your health. It puts extra strain on your heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of developing serious conditions such as heart disease, stroke, kidney problems, and even vision loss. High blood pressure is often called the "silent killer" because it typically doesn't cause noticeable symptoms until complications arise. It is essential to monitor and manage your blood pressure to maintain good cardiovascular health.
The Role of Potassium
How Does Potassium Affect Blood Pressure?
Potassium is an essential mineral that plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy blood pressure level. It acts as an electrolyte in your body, helping to balance the sodium-potassium ratio. Sodium, commonly consumed in the form of table salt, can cause fluid retention and constrict blood vessels, leading to high blood pressure. Potassium counteracts these effects by promoting sodium excretion and relax the walls of blood vessels, thereby lowering blood pressure.
Benefits of Potassium for Blood Pressure
Increased potassium intake has been associated with lower blood pressure levels. Studies have shown that a potassium-rich diet can help reduce both systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The beneficial effects of potassium on blood pressure are particularly notable when combined with a low-sodium diet. By incorporating potassium-rich foods into your daily meals, you can support your cardiovascular health and potentially reduce the risk of developing hypertension-related complications.
Potassium-rich foods
Natural sources of potassium
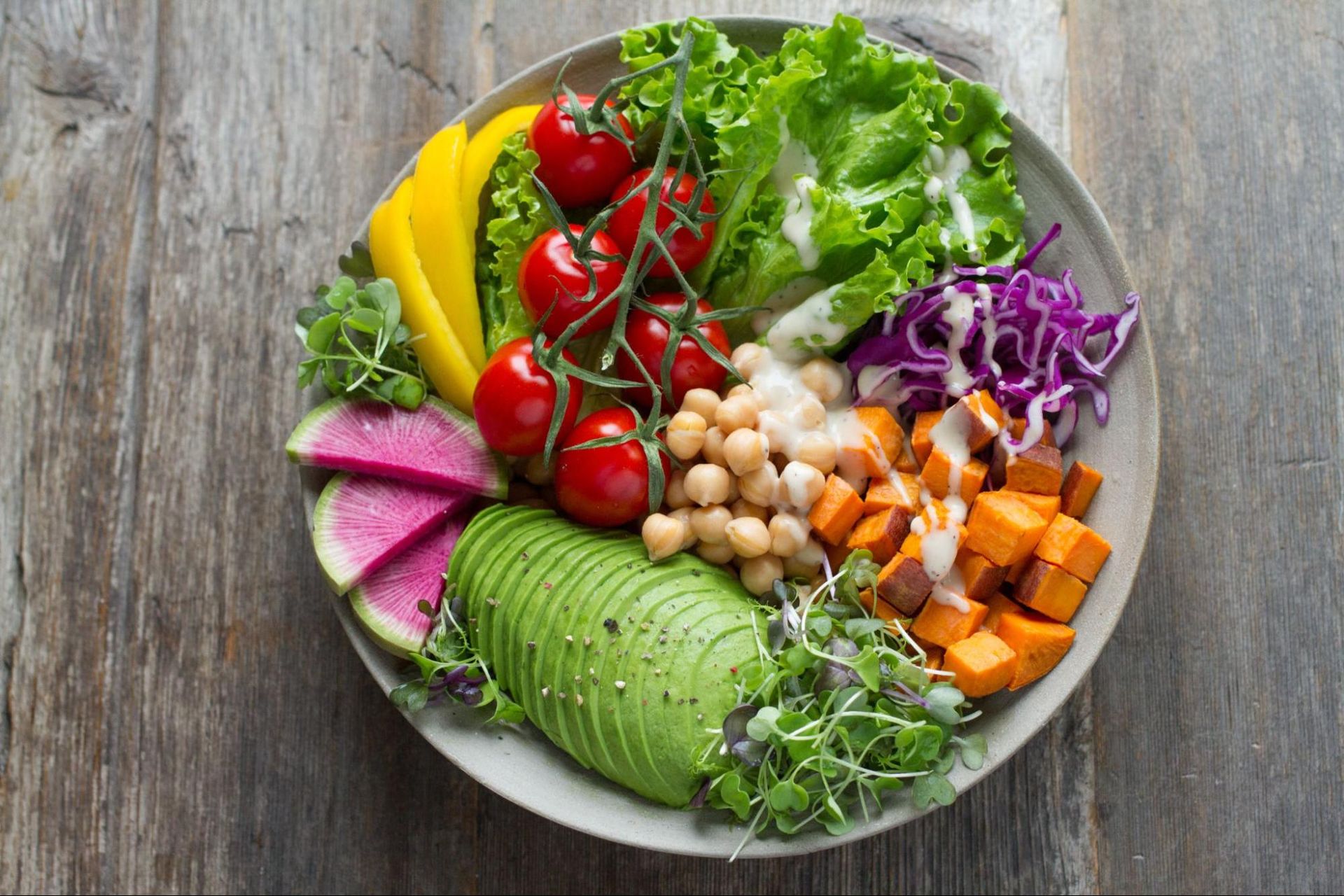

Potassium is found in a wide variety of plant- and animal-based foods. Some of the natural sources of potassium include:
- Bananas: Bananas are well-known for their potassium content. They are convenient, portable, and make for a great snack option.
- Avocados: Avocados are not only delicious but also a fantastic source of potassium. They are packed with healthy fats and can be enjoyed in salads, sandwiches, or as a guacamole dip.
- Spinach: Leafy green vegetables like spinach are rich in potassium. Incorporating spinach into your salads, smoothies, or cooked dishes can boost your potassium intake.
- Sweet Potatoes: These root vegetables are not only delicious but also a great source of potassium. They can be baked, roasted, or mashed as a healthy side dish.
- Oranges: Citrus fruits like oranges not only provide vitamin C but also contain potassium. Enjoying fresh oranges or drinking freshly squeezed orange juice can contribute to your daily potassium needs.
- Tomatoes: Tomatoes are not only versatile but also a good source of potassium. They can be used in salads, sauces, soups, and various other dishes.
- Yogurt: Yogurt is a nutritious food that contains potassium. Opt for plain yogurt or Greek yogurt for a healthier option.
Incorporating these potassium-rich foods into your diet can help ensure you're getting an adequate amount of this essential mineral.
Recommended Daily Intake
The recommended daily potassium intake for adults is around 2,500 to 3,000 milligrams (mg). The potassium requirements of individuals can vary depending on factors such as age, gender, activity level, and overall health. It is best to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian who can assess your specific needs and provide personalized recommendations.
Table: Adequate Intakes (AIs) for Potassium
Age | Male | Feminine | Pregnancy | Lactation
Birth to 6 months | 400 mg | 400 mg | |
7–12 months | 860 mg | 860 mg | |
1–3 years | 2,000 mg | 2,000 mg | |
4–8 years | 2,300 mg | 2,300 mg | |
9–13 years | 2,500 mg | 2,300 mg | |
14–18 years | 3,000 mg | 2,300 mg | 2,600 mg | 2,500 mg
19–50 years | 3,400 mg | 2,600 mg | 2,900 mg | 2,800 mg
51+ years | 3,400 mg | 2,600 mg | |
Note: The values presented in the table represent the Adequate Intakes (AIs) for potassium. These values are approximate and may vary depending on individual needs and health conditions. It is advised to consult a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized recommendations regarding potassium intake.
Increasing your potassium intake through a balanced diet is generally safe for most people. However, individuals with certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease, may require more specific guidance regarding their potassium intake. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure that any dietary changes align with your specific health circumstances.
In the next sections, we will explore how to implement potassium into your diet, lifestyle changes for lowering blood pressure, the dangers of low potassium, and the importance of consulting with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Implementing Potassium into Your Diet
Dietary Changes for Increased Potassium Intake
Increasing your potassium intake can be accomplished by making simple yet effective dietary changes. You can boost your overall potassium consumption by incorporating potassium-rich foods into your meals and snacks. Consider the following suggestions:
- Enjoy a banana as a mid-morning snack.
- Add spinach to your lunchtime salad.
- Experiment with new recipes that include potassium-rich ingredients.
- Include a variety of fruits and vegetables into your meals.
- Get creative with different cooking methods to retain potassium content.
Cooking Methods
Choosing the right cooking methods can help preserve the potassium content in your food. Consider the following techniques:
- Boiling: When cooking vegetables, opt for boiling instead of frying or sautéing. Boiling helps retain the potassium content while still allowing you to enjoy nutritious and flavorful meals.
- Steaming: Steaming is another excellent cooking method that helps retain the natural potassium in your food. This gentle process ensures minimal nutrient loss and results in delicious, nutrient-rich dishes.
- Raw Consumption: Some fruits and vegetables can be enjoyed raw, preserving their potassium content. Eat fresh fruits and vegetables as snacks or salads to maximize your potassium intake.
Lifestyle Changes for Lowering Blood Pressure

Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise and physical activity have proven benefits in lowering blood pressure naturally. Engaging in aerobic activities, such as walking, jogging, cycling, or swimming, can positively impact your cardiovascular health. Strive to engage in a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous exercise each week. Discover activities that you find enjoyable and incorporate them into your regular routine.
Reducing Sodium Intake
Excessive sodium intake can contribute to high blood pressure. To lower your sodium consumption:
- Limit processed and packaged foods, as they often contain high amounts of sodium.
- Opt for fresh, whole foods, which are naturally lower in sodium.
- Use herbs, spices, and other flavour enhancers instead of relying on salt to season your food.
- Be mindful of hidden sources of sodium, such as sauces, dressings, and condiments. Check food labels for sodium content.
Managing Stress Levels
Chronic stress can negatively impact your blood pressure. To effectively manage stress, consider the following strategies:
- Consider practicing relaxation techniques, like deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga.
- Take part in activities that bring you joy, such as pursuing hobbies, reading, or listening to music.
- Seek support from loved ones or consider joining support groups to share your experiences and emotions.
- Prioritize self-care by scheduling activities that help you unwind and relax.
Monitoring Blood Pressure
Importance of Regular Blood Pressure Monitoring
Regular monitoring of your blood pressure is crucial to maintaining your cardiovascular health. Blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day, so tracking it over time provides valuable insights into your overall well-being. Consider the following:
- Invest in a home blood pressure monitor for convenient and regular checks.
- Record your blood pressure readings to monitor any changes or trends.
- Share your blood pressure records with your healthcare professional for analysis and guidance.
- Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to assess your blood pressure and overall cardiovascular health.
The Dangers of Low Potassium
Consequences of Potassium Deficiency
While potassium is beneficial for maintaining healthy blood pressure, having low potassium levels can have adverse effects. Potassium deficiency, known as hypokalemia, can lead to various health issues, including:
- Muscle weakness and cramps.
- Fatigue and general weakness.
- Irregular heart rhythms and palpitations.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Impaired kidney function.
To avoid these consequences, it is essential to strike a balance and maintain an adequate level of potassium in your body. Consulting a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance on maintaining a healthy potassium level is highly important.
Consultation with a Healthcare Professional
Seeking Professional Advice
It is recommended to consult a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your diet or lifestyle. They can assess your individual health status, provide personalized recommendations, and monitor your progress. A healthcare professional can also conduct blood tests to evaluate your potassium levels and overall cardiovascular health, and determine the most suitable approach for your specific needs.
Remember, seeking professional advice is crucial to ensure that any dietary or lifestyle changes align with your unique health circumstances and optimize your blood pressure management.
Conclusion
Lowering your blood pressure naturally is possible with the help of potassium-rich foods and lifestyle modifications. You can take control of your cardiovascular health by incorporating potassium into your diet, engaging in regular exercise, reducing sodium intake, managing stress levels, and monitoring your blood pressure.
FAQs
Q: Can potassium supplements replace potassium-rich foods?
While potassium supplements may be prescribed in certain cases, it is generally recommended to obtain potassium through natural food sources for optimal health benefits.
Q: Are there any side effects of consuming too much potassium?
Excessive potassium intake can be harmful, especially for individuals with certain medical conditions.
Q: Can potassium lower blood pressure immediately?
Potassium alone may not provide immediate results. It is part of an overall healthy lifestyle that contributes to long-term blood pressure management.
Q: Are there any interactions between medications and potassium-rich foods?
Certain medications, such as potassium-sparing diuretics, can interact with high-potassium foods. It is essential to discuss potential interactions with your healthcare provider.
Q: How long does it take to see improvements in blood pressure through lifestyle changes?
Results may vary, but positive changes in blood pressure can often be observed within a few weeks of implementing lifestyle modifications. Persistence and consistency are key.